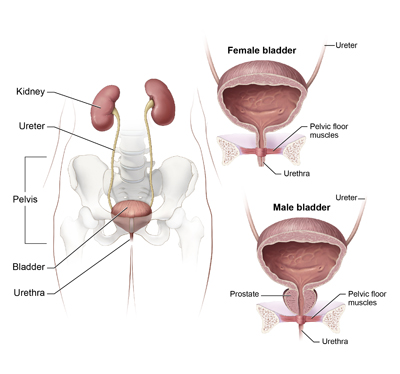
Cystitis is an inflammation of the bladder, most often as a result of a urinary tract infection (UTI) caused by bacteria entering the bladder or urethra and multiplying. Bladder infections are painful annoying, and if left untreated, can spread to your kidneys.
In women especially, this may occur as a result of sexual intercourse, hormonal changes due to either pregnancy or menopause, and from certain types of birth control, like a diaphragm. But even sexually inactive and younger females are susceptible because the female genital area often harbors the bacteria that can cause cystitis, and a shorter urethra than men means a shorter distance for that bacterium to travel to the bladder.
While bacterial infections are the most common cause of UTIs, there are a number of noninfectious factors that may cause cystitis. Here are some possibilities:
• Interstitial cystitis – chronic or long-term case affecting multiple layers of bladder tissue
• Drug-induced cystitis – inflammation due to certain medications, especially chemotherapy drugs
• Radiation cystitis – radiation treatment to the pelvic area can damage bladder tissue leading to inflammation
• Chemical cystitis – may be developed due to an allergic-type reaction by people with hypersensitivity to chemicals contained in certain products, i.e., bubble bath, feminine hygiene sprays or spermicidal jellies
• Foreign-body cystitis – inflammation caused by long-term use of a catheter
• Cystitis affiliated with other conditions – can co-occur with other disorders like diabetes, kidney stones, spinal cord injuries or an enlarged prostate.
Symptoms
Cystitis signs and symptoms often include:
• Frequent urge to urinate; urgency to urinate after an empty bladder
• Burning sensation when urinating
• Blood in the urine
• Cloudy or strong-smelling urine
• Pelvic discomfort
• Cramping, pressure in the lower abdomen or back
• Low-grade fever
• Pain during sexual intercourse
In young children, new episodes of accidental daytime wetting also may be a sign of a urinary tract infection; nighttime bed-wetting on its own isn’t likely to be associated with a UTI.
Facial Signs of Cystitis
Indications of the presence of cystitis can show up first on the face, especially:
• Dark circles under eyes
• Skin blemishes
Testing and Treatment
A cystitis diagnosis is determined from testing a urine sample to check for a UTI, or by imaging through a medical cytoscope. Treatments are very successful and are used to address the presenting symptoms, relieve pain, and prevent reoccurrence. These range from antibiotics and over-the-counter pain relievers (e.g., ibuprofen and acetaminophen), to sitz baths to cleanse the pelvic area and drinking lots of fluids.
At our clinic, a specific treatment plan is designed to tackle each patient’s individual needs. Our Functional Medicine approach seeks to address the root causes as well as manage the conditions naturally through dietary adjustments and herbal supplements, as well as with lifestyle changes, acupuncture and other protocols. For cystitis, these methods include the following:
• BIOSET
• Cupping
• Electro Dermal Screening
• Food and Environment Sensitivity
• Organ Detoxification & Restoration
