Celiac disease is a serious autoimmune disease that occurs in genetically predisposed people where the ingestion of gluten—a protein found in wheat, barley and rye—leads to damage in the small intestine. Eating gluten triggers an immune overreaction, which over time harms the intestinal lining and prevents it from absorbing important nutrients (malabsorption) into the body.
Celiac disease is hereditary and can develop at any age. Left untreated, it can lead to additional serious health problems, such as malnutrition, osteoporosis, infertility, and cancer. In children, malabsorption can affect growth and development. While there is currently no cure for celiac disease, it can be largely managed for most people by following a strict gluten-free diet and bolstering gut health.
Symptoms
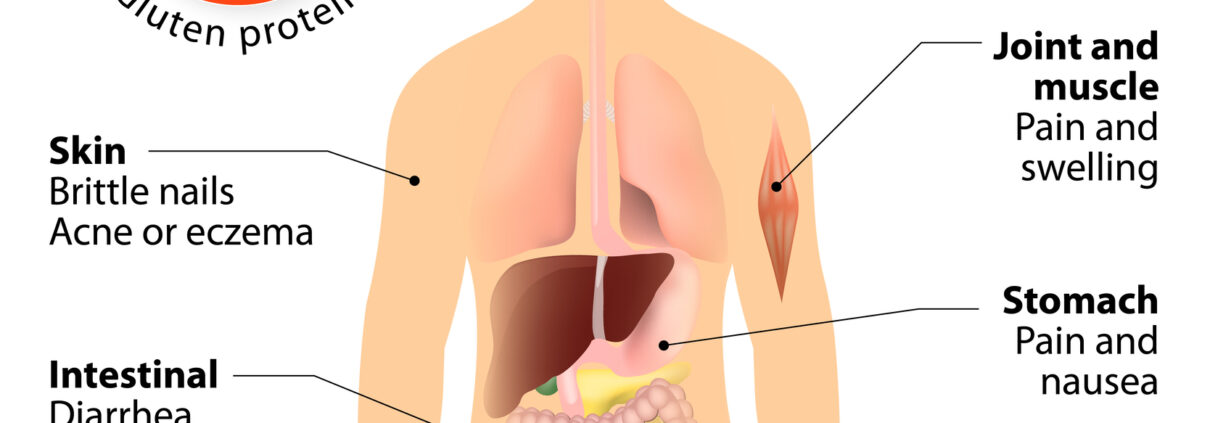
The signs and symptoms of celiac disease can vary greatly and differ in children and adults. Digestive signs and symptoms for adults include:
• Diarrhea
• Weight loss
• Bloating, gas and abdominal pain
• Nausea and vomiting
• Constipation
However, more than half the adults with celiac disease have signs and symptoms unrelated to the digestive system, including:
• Joint pain
• Mouth ulcers
• Headaches and fatigue
• Anemia, usually from iron deficiency
• Impaired spleen functioning (hyposplenism)
• Loss of bone density (osteoporosis) or softening of bone (osteomalacia)
• Itchy, blistery skin rash (dermatitis herpetiformis)
• Nervous system injury, including numbness and tingling in the feet and hands, possible problems with balance, and cognitive impairment
In addition to the digestive problems already listed above, children with celiac disease are more likely than adults to also have swollen bellies and pale, foul-smelling stools. And the inability to absorb nutrients might result in:
• Failure to thrive for infants
• Damage to tooth enamel
• Weight loss
• Anemia
• Irritability
• Short stature
• Delayed puberty
• Neurological symptoms, including ADHD, learning disabilities, headaches, lack of muscle coordination and seizures.
Facial Signs of Celiac Disease
Indications of celiac disease can appear on the face with the presence of the following:
• Rosacea
• Pale complexion
• Flushing
• Rashes
• Acne
Testing and Treatment
Many people don’t realize they have celiac disease, so blood testing and genetic testing are important first steps for proper diagnosis before starting a strict gluten-free diet. At our clinic, our testing and treatment methods are rooted in holistic and Functional Medicine principles. We assess patient history, examine test results, and manage the condition naturally through gluten-free dietary adjustments and nutritional supplements for support and to boost good gut health. We also provide recommendations for lifestyle changes that support health goals.
We address immediate symptoms and pursue long-term solutions with acupuncture and other protocols. Depending on individual patient needs, our testing and treatment modalities may include:
• BIOSET
• Cupping
• Electro Dermal Screening
• Food and Environment Sensitivity
• Organ Detoxification & Restoration
• Weight Loss and Nutrition Counseling
All testing and treatment methods are noninvasive, without side effects, and are well tolerated by adults and children.
